You do not need to draw nonbonding electrons. So our die peptide will be Oh double Bond.

Peptide Bond Definition Structure Mechanism And Examples
Draw the hydrogen bonding typically found between two residues in an α helix.

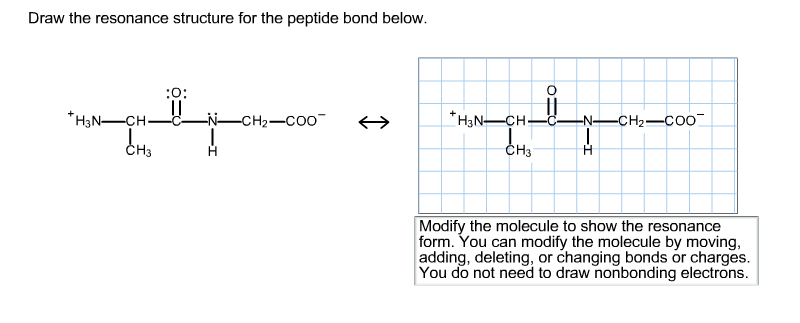
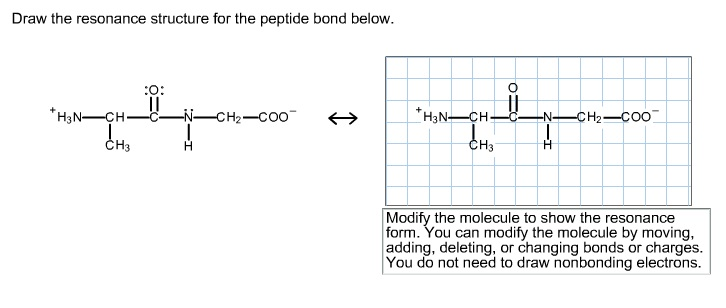
. 4 Why glycine and proline are often found within a beta-turn. Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond below. Thus the peptide unit is a planar rigid structure and rotation in the peptide backbone is restricted to the bonds involving the a carbon.
The rigid planar nature of the peptide unit has. The peptide bond would be right here. 3 Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond and explain why there is no rotation around the C-N bond.
Biology questions and answers. Protein phosphorylation is an example of what. Draw the hydrogen bonding typically found between two residues in an a helix.
Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond below. The real structure of course is a weighted hybrid of these two structures. Draw a dipeptide of two amino acids in trans linkage side-chains can be shown as and indicate which six atoms are part of the planar structure of the peptide.
The real structure of course is a weighted hybrid of these two structures. Therefore a reasonable resonance structure can be draw with a double bond linking the carbon and nitrogen and which result in a negative charge on the oxygen and a positive charge on the nitrogen. View the full answer.
HN-CHC_NCH-COO- Сн н C -. The C-N distance in a peptide bond is typically 132 Å which is intermediate between the values expected for a C-N single bond. The four atoms that are part of the peptide bond are shown as larger spacefilling models.
Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence from N- to C-terminus determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The resonance structure prevents rotation around the peptide bond. The intermediate resonance structure imparts a partial double bond characteristic to the CN bond thereby prohibiting rotation.
1 Pauling and Corey showed that in small peptides six atoms associated with the peptide bond all lie in a plane. Draw The Resonance Structure Of A Peptide Bond. Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond and explain why there is no rotation around the C-N bond.
The dashed lines indicate the resonance of the peptide bond. Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond shown in the image. 24 is asking us to draw the resident structures of the peptide bond so we can start by trying are a peptide bond.
Click on the structure below to switch the resonance forms of the peptide bond. Modify the molecule by moving adding deleting or changing bonds or charges to show the resonance form. The stability of the peptide bond as well as other properties important for the behavior of polypeptides is due to resonance the delocalization of electrons over several atoms.
Meanwhile the basic groups terminal amino group and R group of. You can modify the molecule by moving adding deleting or changing bonds or charges. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
Lets draw the structure of the die peptide glycerine and serene. Draw the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids. First it increases the polarity of the peptide bond.
The Edman Degradation 267 Peptide Synthesis 268 Automated Peptide Synthesis. The formation of a peptide bond is what type of reaction. And then to get the residents structure we can move the electrons from this double bond up to the oxygen that we can move this lone pair from nation between the carbon and nitrogen.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. The structure at the right shows a peptide bond between the amino acids valine Val and serine Ser. The resonance structure prevents rotation around the peptide bond.
Draw a dipeptide of two amino acids in trans linkage side-chains can be shown as R and indicate which six atoms are part of the planar structure of the peptide bond. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide bonds. Overview of protein structure Page.
The resonance structure is a significant factor in depicting the true electron distribution. The structure of the peptide KHNP at pH 7 is shown below. So theres air Die peptide and were asked to circle the peptide bond.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond If subtlety isnt your thing Choose some thing with a little bit more bling. The amide structure has two resonance contributors.
Therefore a reasonable resonance structure can be draw with a double bond linking the carbon and nitrogen and which result in a negative charge on the oxygen and a positive charge on the nitrogen. Select Draw Rings Groups More Erase. Who are the experts.
Modify the molecule to show the resonance form. The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids which is connected by the p. Isoelectric Points 263 Synthesis Of Amino Acids 264 Peptides And Proteins 265 Amino Acid Analysis Of Peptides 266 Peptide Sequencing.
KHNP is also known as lysylhistidylasparagylproline where the lysine residue is the N-terminal and the proline residue is the C terminal. From text to jewels and also chains theres no limit into the 3D components you could attach on your nails so get Innovative and Allow loose. 3 Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond and explain why there is no rotation around the C-N bond.
Because the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen has a partial double bond character rotation around this bond is restricted. 261 Structures Of Amino Acids 262 Amino Acids And The Hendersonhasselbalch Equation. The intermediate resonance structure imparts a partial double bond characteristic to the CN bond thereby prohibiting rotation.
The Merrifield Solid-phase Method 269. Oh and H the bond Oh eight and H two. Resonance has two other important consequences.
Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond and explain why there is no rotation around the CN bond. Two Cα atoms which are diagonally opposite relative to the CN bond. Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond and explain why there is no rotation around the CN bond.
The atoms C H N O of the peptide bond lies in the same plane like the hydrogen atom of the amide group and the oxygen atom of the carboxyl group are trans to each other. 24 is asking us to draw the resident structures of the peptide bond so we can start by trying are a peptide bond. The amino acids are taken from the crystal structure of hemoglobin αVal 132 and αSer 133.
Resonance structure of peptide bond Peptide Bond A peptide bond is a covalent bond found in the primary structure of a protein. Do not draw nonbonding electrons. The dipole momentof each peptide bond is shown in Figure 1-8.
Chemistry questions and answers. The coplanarity of the peptide bond denotes the resonance or partial sharing of two pairs of electrons between the amide nitrogen and carboxyl oxygen. At pH 7 all of the acidic groups terminal carboxyl group and the R group of histidine are deprotonated.
We review their content and use your feedback to. Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond. Chapter 4 The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins 47 40.
This problem has been solved.

Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com
Peptide Bonds Biochemistry Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Proteins Openlearn Open University
Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com

Peptide Bond Essentials Biochemistry Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Converting Fischer Projection To Bond Line Structure Using The R And S And Swap Method Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Classroom
Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com

Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com
0 comments
Post a Comment